BTO GBW NE pilot

This project is available for public Spotting but Trapping is restricted. If you would like to join this project as a Trapper please contact us at info@mammalweb.org.
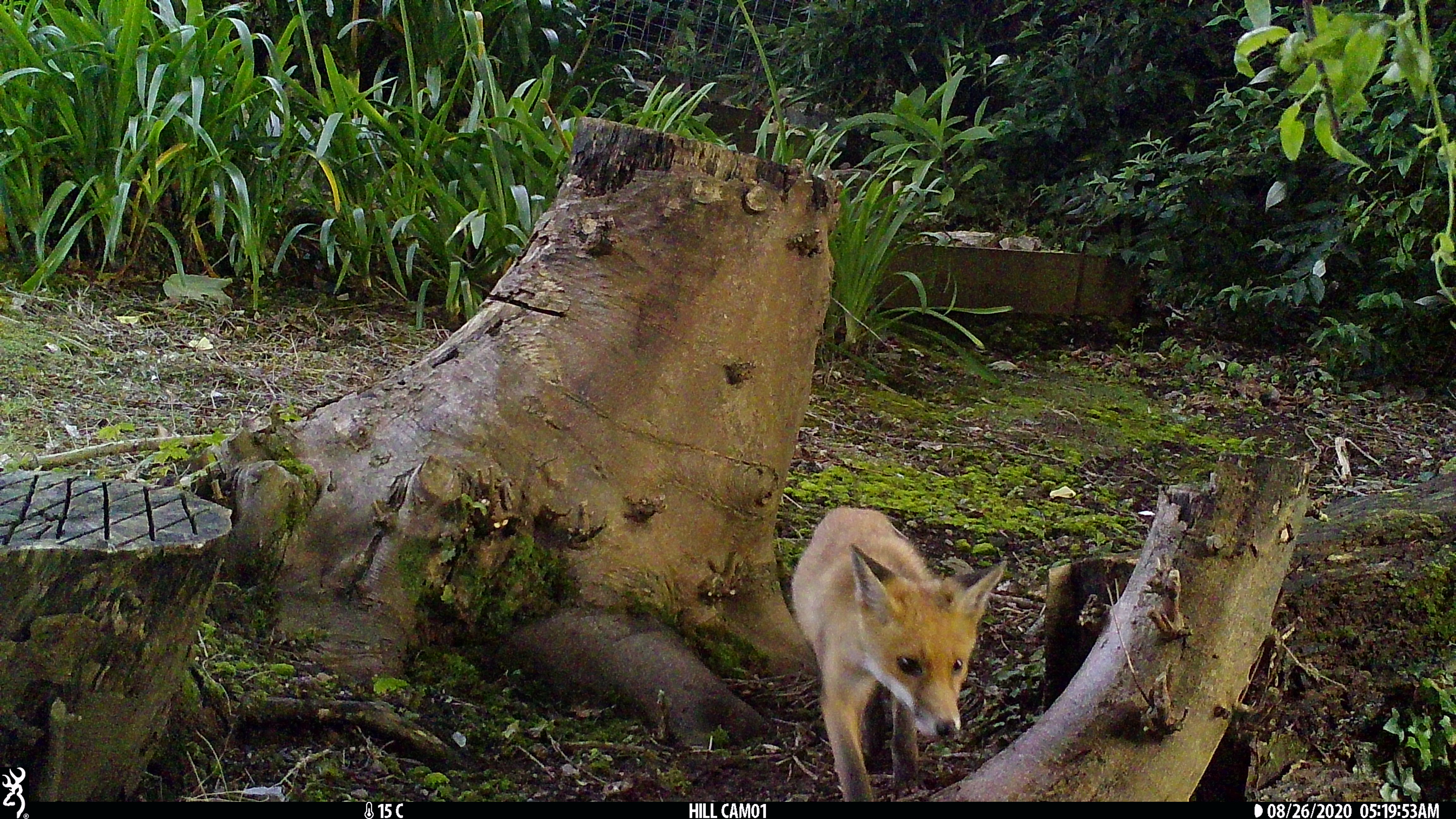
The North East pilot study aims to determine the best camera trap placements in gardens for monitoring wildlife.
Understanding bird-mammal interactions is vital for revealing significant ecological relationships such as predation, competition, and mutualism, which greatly impact ecosystem structure and function. Urban environments create unique ecological pressures and opportunities that can change traditional wildlife behaviours and interactions. For example, changes in habitat availability and food resources can influence predation dynamics, competition, and even symbiotic relationships between birds and mammals. Studying these interactions helps in developing effective urban wildlife management and conservation strategies.
Urban home gardens are ideal for these studies, and camera traps offer the best way to capture these interactions without disturbing them. Unfortunately, no studies have been conducted in home gardens using camera traps to understand garden wildlife interactions. This pilot study aims to determine how efficient camera trapping and their placements in home gardens can significantly aid in understanding and conserving our local urban wildlife. This pilot will also help refine how we could work with Garden BirdWatch participants across the UK for the MammalWeb-BTO Garden BirdWatch project in the future.
If you have any questions about the project or how to support the image classification process then feel free to contact Afthab at afthab.f.katakath@durham.ac.uk.

 English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)  Czech (Čeština)
Czech (Čeština)  Nederlands (nl-NL)
Nederlands (nl-NL)  Magyar
Magyar  Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)  Croatian (Hrvatski)
Croatian (Hrvatski)  Polski (PL)
Polski (PL)  Español (España)
Español (España)